Key Takeaways
- Google’s AI Mode delivers conversational, multimodal, and personalized search results.
- Website traffic from basic informational searches is likely to decline, but deeper engagement may increase.
- SEO strategies must shift toward structured, authoritative, context-rich content.
- Content creators should prioritize multimodal content (articles, videos, visuals, interactive tools).
- Brand visibility through AI citations and mentions becomes crucial.
- Lead generation funnels shorten; optimizing immediate value and clear calls-to-action is essential.
- Businesses should integrate extensively with Google’s tools and ecosystem for maximum benefit.
- Introduction
- What Is Google’s AI Mode?
- How Does AI Mode Work?
- What Does AI Mode Look Like? (User Experience)
- Impact on Website Traffic & Visibility
- Impact on SEO Strategies & Ranking Factors
- Impact on Content Formats (Blog, Video, Interactive Content)
- Impact on Engagement & Brand Discovery
- Impact on Lead Generation Funnels
- Strategies for Content Creators & Small Businesses to Adapt
- Google’s AI Mode vs. Bing Copilot vs. Perplexity: A Brief Comparison
- Conclusion
- Methodology
- Resources
Introduction
Google’s experimental AI Mode, introduced via Search Labs in 2025, transforms the traditional search experience into an interactive, AI-driven conversational assistant powered by Google’s Gemini 2.0 AI. Unlike standard search or static AI Overviews, AI Mode synthesizes comprehensive, real-time information using advanced multimodal reasoning, personal context, and query fan-out (parallel related searches). For U.S.-based content creators and business owners focused on audience engagement and lead generation, adapting to AI Mode’s significant impacts on search traffic, SEO, content visibility, and user engagement patterns is crucial.
This report explains what AI Mode is, how it works, and what it means for U.S. business owners and content creators who rely on search traffic for audience engagement and lead generation. We’ll break down AI Mode’s technology (like Gemini 2.0, multimodal reasoning, and query fan-out) in non-technical terms, compare it to traditional search and Google’s AI Overviews, and analyze its impact on website traffic, SEO strategy, content formats, engagement, and lead funnels. Finally, we’ll provide actionable tips to help you stay visible and valuable in this new search environment.
What Is Google’s AI Mode?
AI Mode is an experimental, conversational search experience within Google (launched via Search Labs in 2025) that uses advanced AI to answer your queries in a chat-like format. Instead of simply showing a list of websites, AI Mode provides an AI-generated answer to your question, with the ability to ask follow-up questions and dig deeper into the topic. In essence, it’s Google’s way of embedding a powerful chatbot (powered by Gemini 2.0, Google’s latest AI model) directly into search.
- Traditional Search: You enter a keyword or question and get a page of ranked results (links to websites) that you sift through. The search results are static and largely the same for everyone (with minor personalization).
- AI Overview (SGE): In 2023–2024, Google introduced AI-generated snippets on the results page (“AI Overviews”) that summarize answers above the links. These overviews are short summaries with cited sources, but interaction is limited – you might get a few suggested follow-up questions to click.
- AI Mode: This is a dedicated search mode or tab where the search engine behaves like an interactive AI assistant. You ask a question and get a rich, conversational answer (often a few paragraphs) instead of the usual list of links. You can then refine or follow up with another question in a natural dialogue. In AI Mode, Google’s AI can handle more complex, multi-part questions and reasoning tasks that would normally require several separate searches. It’s like chatting with an expert who can instantly comb through the entire web for you.
Why AI Mode? Google found that many power users wanted AI help for a wider range of searches, beyond what the basic AI Overviews offered. AI Mode is designed for those tough or exploratory questions where a one-shot answer isn’t enough. It leverages a custom version of Gemini 2.0 (Google’s cutting-edge AI model) to provide more in-depth reasoning, comparisons, and even to handle multimodal queries (questions involving text, images, or other media). In other words, AI Mode can “think” through a problem with you, using the breadth of Google’s real-time information sources, and deliver an answer with citations and next-step suggestions.
How Does AI Mode Work?
Under the hood, AI Mode uses several advanced technologies and techniques to retrieve and synthesize information. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and how they differ from a normal Google search:
- Gemini 2.0 – Google’s Advanced AI Brain: AI Mode is powered by Gemini 2.0, a next-generation large language model (LLM) developed by Google. This model is like an AI brain that has been trained on vast amounts of text (and code, images, etc.), enabling it to understand complex questions and generate human-like answers. Compared to earlier models, Gemini 2.0 has enhanced reasoning abilities and supports multimodal input (it can interpret and generate more than just text). In AI Mode, a custom version of Gemini 2.0 is used to plan answers, perform calculations or coding queries, and even handle image-related questions. This means if you ask something like “Compare these three products and show me a chart,” AI Mode’s underlying model is capable of doing that analysis and even producing a visual or detailed breakdown as part of the answer (something traditional search couldn’t do directly).
- Multimodal Reasoning: Unlike text-only search, AI Mode can natively work with multiple types of content. It can incorporate text, images, audio, video transcripts, and more into its answers. For example, if a user asks, “How do I fix a leaky faucet?” AI Mode might pull up a how-to video (or its transcript) in addition to text instructions. It might even use Google’s MUM (Multitask Unified Model) to translate information from other languages if it’s relevant. This multimodal support means content creators should consider that all formats (blog articles, images, videos, podcasts) can be accessed and integrated by the AI. The AI doesn’t just read web pages like a person would – it can also “watch” videos or “listen” to podcasts in a sense, because it analyzes their transcripts and content. Every response in AI Mode is a blend of different media and sources, dynamically assembled in real time, rather than a simple list of text documents.
- Query Fan-Out (Parallel Searching): One of AI Mode’s core innovations is something Google calls “query fan-out.” Instead of taking your question and doing one search through the index, AI Mode breaks your query into many related sub-queries and searches for each of those in parallel. Think of it as the AI brainstorming all the related questions you might have meant or follow-up questions you might ask next. It then quickly Googles all of those for you behind the scenes. This way, it can gather a constellation of facts and perspectives at once. Why? Because people’s questions often have multiple facets. For instance, if you ask, “What’s the best electric SUV for a family of five?” a traditional search might look for “best electric SUV” and give general results. AI Mode, through query fan-out, might secretly also search “safety ratings of electric SUVs,” “electric SUV seating 5 comparison,” “family car electric SUV reviews,” etc., without you explicitly asking. By issuing multiple searches concurrently across subtopics and sources, the AI captures details you didn’t explicitly request, then fuses them into a single, richer answer. This technique allows Google to surface a broader and deeper range of information than a single search query would.
- Reasoning and Chain-of-Thought: AI Mode doesn’t just fetch facts; it reasons through information. Google’s AI will often perform a multi-step thinking process (internally) to answer complex questions. It’s as if the AI is having an internal dialogue or “arguing with itself,” examining different pieces of data to construct a logical answer. For example, if you ask a complex question like “Should I lease or buy a car for my new business?”, AI Mode might break this down into sub-problems: current interest rates, tax implications of leasing vs buying, average mileage you’ll drive, etc., gather information on each, and then synthesize a recommendation. This is often referred to as “chain-of-thought” reasoning. The AI selects content not just because it’s relevant to the keywords, but because it fits a point in the AI’s reasoning chain – essentially, each source might be used to support one step of the answer’s logic. This is a big shift from traditional SEO where if you ranked #1, you got the click; now your content might be used because it answers one part of a larger question.
- Personal Context & Memory: Perhaps most striking, AI Mode can personalize results based on the user’s context and history. It is “memory-aware,” meaning it remembers the conversation you’ve had so far and who you (the user) are, to some extent. Google has indicated it will draw on personal data (with permission) from across your Google ecosystem – for example, Gmail, Google Calendar, or other apps – to tailor answers. In practical terms, two users asking the exact same question in AI Mode might get different answers or different cited sources, “not because of ambiguity in the query, but because of who they are”. The AI could incorporate knowledge of your preferences, location, or past searches. For instance, if you search for “good restaurants for a client meeting,” AI Mode might use your Calendar and Gmail (personal context) to know where your meeting is or what cuisines you like, then give a recommendation. This personalization goes beyond what traditional Search and even AI Overviews did. It implies that ranking in AI Mode isn’t one-size-fits-all – Google might choose content that best aligns with the user’s profile, not just overall popularity. The AI also maintains conversation memory, so if you asked a question last week and reference “that solution you gave me” today, it can recall what you talked about earlier (Google hints at some form of long-term conversational memory in the system prompt). For content creators, this means the context in which your content appears could depend on the user’s prior interactions.
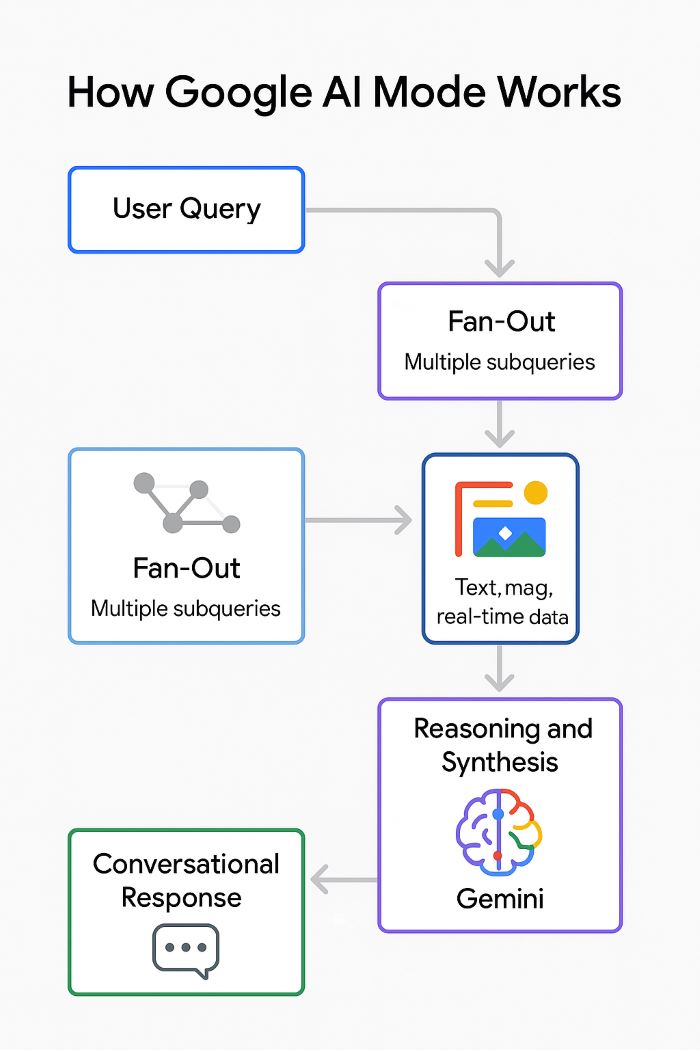
- Citations and Source Selection: AI Mode does provide citations (links) to sources, much like AI Overviews do, but how sources are chosen is more complex. The AI isn’t just listing the top 10 websites anymore; it’s selecting snippets from various pages that best support its answer. Importantly, inclusion as a cited source now depends on semantic relevance and factual credibility rather than just keyword matching or even traditional authority alone. In fact, being cited in an AI answer is somewhat probabilistic – the AI might draw from dozens of sources internally but only show a few citations, and those can vary by user or phrasing. Google’s system may favor content that fits the embedding profile (AI’s understanding) of the user’s query and context. This means your content has to align closely with the user’s intent and the AI’s interpretation to get picked up as a reference. Later in this report we’ll discuss strategies to increase your chances of being cited by the AI.
In summary, AI Mode is an AI-first search experience: it uses a powerful model (Gemini) that can reason, search broadly, and personalize the results, giving users a single conversational answer that feels like talking to an expert. Next, let’s visualize what this actually looks like for a user.
What Does AI Mode Look Like? (User Experience)
From a user’s perspective, AI Mode turns Google into a conversational assistant. On the Google website or app, AI Mode typically appears as a separate “AI” tab or mode in the search interface (as of 2025, it’s a tab available to all U.S. users). When activated, the interface changes from the standard list of results to a chat-style layout. Here’s how it functions:
- Conversational Q&A Format: In AI Mode, the top of the search page features an AI-generated answer to your query in a few paragraphs of natural language, rather than the usual snippet plus link. It often already anticipates follow-up questions you might have. For example, if you ask “How do I improve my credit score?”, AI Mode might answer with a step-by-step explanation and also mention related tips like managing credit card utilization or checking credit reports – essentially answering the next question (“how exactly do I do that?”) before you even ask. Below this answer, there may be suggestions like “Follow up: How long does it take to rebuild credit?” which you can click or ask. The experience is interactive – you can type a clarifying question or ask for more details, and the AI will remember the context and continue the conversation.
- No “10 Blue Links” – But There Are Citations: The AI’s answer typically includes footnote numbers or hyperlinks embedded in the text that correspond to sources (web pages). Instead of showing full URLs in the answer text, you might see statements like “According to a recent study, doing X can raise your score by 50 points【source】.” If you click that citation, it will open the source website. So, web content is still behind the answers, but it’s one step removed. Google’s UI might show a few traditional results or a carousel of “Learn more” links below the AI answer, but the primary focus is the AI’s summary. This means a user could get what they need without scrolling down to the regular results at all. Notably, Google reports that over a billion people have tried these AI features already, indicating users are indeed engaging with these AI answers.
- Iterative Search Made Easy: AI Mode encourages users to refine their query by simply continuing the dialogue. There’s usually a chat box or prompt like “Ask a follow-up”. You don’t have to start a new search; you just ask your next question. This is different from traditional search where each query was separate – here, it’s a persistent thread. For instance, after the credit score answer, you could type “What about if I have no credit history?” and the AI will incorporate that context rather than treating it as a brand new query. This iterative approach keeps users on Google longer, engaging with the AI.
- Multimodal Responses and Tools: Google’s AI Mode interface is evolving to handle different media. While much of the interaction is text-based Q&A, the AI can also present information in other formats when helpful. For example, if you ask a data-heavy question, AI Mode might display a chart or graph within the answer. If you search for how to do something, it might show an image (or a short video clip) alongside the explanation. Google demonstrated support for complex analyses and visualizations in AI Mode – meaning the AI could, say, analyze a dataset and generate a graph on the fly as part of its answer. There’s also mention of a “Search Live” feature in AI Mode, suggesting it can pull in up-to-the-minute information (like live sports scores or stock prices) into the conversation – something traditional search would do via specialized boxes or not at all in the same integrated way.
- Integration with Other Google Services: AI Mode is more personalized thanks to integration with Google’s ecosystem. The interface might proactively use info from your Gmail, Calendar, Maps, etc., to tailor results (with your consent). For example, if you ask “Plan a one-day itinerary in New York City,” AI Mode could cross-reference your Gmail for any hotel or flight bookings, use Maps data for attractions near you, and then present a custom plan. This is part of the “personal context” we discussed – the user interface might feel like a personal assistant that knows your schedule and preferences. For business owners, this hints that user-specific results could trump generic ones. A local business might be recommended to a user because that user’s past behavior indicates they’d prefer it, even if that business isn’t the top SEO result generally.
- AI Agents and Actions: A forward-looking feature in AI Mode is the introduction of AI agents – essentially, the AI not only recommends but can help execute tasks. Google has hinted at (and demoed) scenarios where AI Mode can actually do things like book reservations or purchase items on your behalf right from the search interface. For example, if you typed “Book me a table for two at an Italian restaurant in downtown tonight,” AI Mode could split this into sub-tasks, search for available restaurants, and even complete the reservation without you ever leaving the search page. Similarly, “Find and buy two tickets to a Lakers game next week” might lead the AI to search ticket sites, compare prices, and help you complete the checkout within Google. These “agentic” capabilities are experimental, but Google’s Project “Mariner” and others suggest this is coming. The UI in these cases becomes more interactive and form-like, guiding you through the steps with the AI’s help. For users, this is extremely convenient; for businesses, it’s a new paradigm where conversions might happen entirely on Google’s platform.
Bottom line: AI Mode’s interface feels like chatting with a knowledgeable assistant. It’s designed to give users direct answers (with source links available) and let them accomplish tasks without multiple searches or clicks. Next, we’ll discuss what this means for the visibility of websites and the flow of traffic, since the AI is effectively sitting between users and your content.
Impact on Website Traffic & Visibility
One of the biggest questions for content creators and business owners is: “If Google is answering questions with AI, will people still visit my website?” The short answer is expect a decline in direct clicks from many informational searches, but the dynamics of traffic are changing in nuanced ways.
- Reduced Click-Through Rates: Studies and early data are showing a significant drop in clicks to websites when an AI overview or answer is present. In fact, an analysis by Ahrefs found that Google’s AI Overviews (the summaries at the top of search results) reduced clicks to websites by about 34.5%. This means if 100 people used to search a query and, say, 50 would click an organic result, now perhaps only ~33 people click a result, because the others got their answer from the AI without needing to leave Google. Google initially claimed AI features could increase clicks, but independent logic and research disagree – people tend to click less when their query is answered directly on the results page. As AI Mode rolls out, which provides even more comprehensive answers than the simple overviews, we can anticipate a further shift from click-outs to on-page consumption. In practical terms, your website might see traffic drops for queries that can be satisfied by a quick answer or summary (think FAQs, simple how-tos, fact-based questions).
- Visibility vs. Traffic: It’s not all doom and gloom, however. Your content can still be “seen” via citations even if the user doesn’t click through immediately. Being one of the cited sources in an AI answer is becoming a valuable form of visibility. It’s a bit like being quoted as an expert in an article – even if the reader doesn’t immediately seek out your site, your brand gains exposure. For example, if Google’s AI answers a question about homebuying and includes “According to YourSite.com, first-time buyers should save at least 20%,” the user sees your brand name. That impression has marketing value. In the past, if you didn’t get the click, you got nothing. Now, you might get a mention without a click. So, brand visibility can continue (or even improve) while traffic drops. In an analysis of 8,000 AI-generated answers, it was found that AI systems often cite sources that demonstrate expertise and trustworthiness. This means if you can become a preferred source for the AI, you maintain visibility.
- “First Touch” vs “Last Touch” Traffic: Consider that AI Mode might handle the top-of-funnel information gathering. Users ask broad questions, get general answers (with your content potentially woven into those answers), and only click through when they need more depth or a specific service. The traffic that does come to you may be more qualified. Google has suggested that while clicks are fewer, those clicks might be from users who are deeper in the decision process, making them more valuable. (In fact, Google hinted at focusing on “the improved quality of visits” and even advised to “stop measuring clicks” so religiously!). For instance, someone might use AI Mode to learn “what is cloud accounting software?” and get an overview. If your site is cited, they learn your brand exists. Later, when they ask the AI “who offers the best cloud accounting solution for a small business?” they might see your brand again or decide to click your site that time. So, you may get fewer overall visitors from these AI-assisted searches, but those who do arrive are better primed (they’ve effectively been pre-educated by the AI, possibly with your help).
- New Metrics of Success: As AI Mode becomes common, traditional SEO metrics like click-through rate (CTR) and even rank tracking need rethinking. If AI Mode becomes the default search experience (which it likely will in the future), the concept of “ranking #1” for a keyword changes. Your page might rank behind the scenes (in the AI’s retrieval list) without a visible “#1” spot. A more pertinent metric might be “AI citation share” – how often and prominently your content is cited by AI answers. Google’s Search Console is planning to report on AI Mode performance, which suggests impressions and clicks from AI results will be tracked. However, early indications are that this data may not be granular (you might see AI Mode traffic blended into your reports, not as a separate filter). For now, keep an eye on overall organic traffic and any uptick in branded searches or direct traffic, which could result from users seeing your brand in answers and later visiting.
- Possible Traffic Redistribution: AI Mode might reduce organic clicks, but some traffic could shift to other channels. For example, if a user engages deeply with an AI and then uses a provided link to go to a site, they might be a more serious visitor (as mentioned). Also, if AI Mode encourages more complex queries (because people see they can ask detailed questions), there may be new long-tail queries that your site can appear for (either as citations or in the remaining organic links). Additionally, some users, when faced with an AI answer, might scroll past it for a second opinion, clicking on an organic result out of skepticism or desire for more detail. In niches where trust is critical, being ranked just below the AI box might still get decent clicks from users double-checking the AI.
Key takeaway: Expect an overall decline in raw traffic from informational queries, around 30-40% drop in some cases where AI answers suffice, but the traffic you do get may be more qualified and conversion-prone. Visibility will increasingly come from being referenced by the AI, which is a new kind of “SEO win.” In response, businesses should diversify how they reach audiences (e.g., building email lists, social, etc., not just relying on Google clicks) and focus on strategies to become the cited authority in AI answers (more on that in the strategy section).
Impact on SEO Strategies & Ranking Factors
With AI Mode changing how content is retrieved and presented, the rules of SEO are evolving. Here’s how SEO strategy and ranking factors are impacted:
- Semantic and Contextual Optimization Over Keywords: Traditional SEO often revolved around specific keywords – you target “best laptop 2025” and try to rank for that exact term. AI Mode cares less about exact keywords and more about the underlying meaning and context. Because of query fan-out, Google’s AI might rewrite or decompose a query into dozens of variations. It’s looking for content that semantically answers the question, even if it doesn’t use the exact phrasing. For SEO, this means you should focus on covering topics comprehensively and naturally, rather than obsessing over one keyword phrase. Latent semantic indexing (LSI) keywords, synonyms, related questions – all that becomes table stakes. Essentially, your content should aim to answer the user’s intent broadly, covering subtopics that the AI might explore. As iPullRank’s analysis puts it, “You’re no longer optimizing for a specific keyword or even a specific page. You’re optimizing for your content to be relevant across dozens of hidden queries… Your ranking is probabilistic, not deterministic.”. In practical terms, ensure your content is rich and covers the who/what/why/how of a topic, since the AI will be pulling bits to answer various offshoot questions.
- E-E-A-T and Authority Matters Even More: E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness, and it has been a Google guideline for content quality. In AI Mode, where the algorithm is picking sources to trust in crafting an answer, having strong E-E-A-T signals is critical. Analyses of AI citations have shown that AI models prefer to cite content that demonstrates clear expertise and credibility. For example, content written by a recognized expert (with a bio stating credentials) or backed by data and authoritative references tends to be favored. One study found that pages with author bios showing credentials were cited 3× more often by AI, and getting backlinks from authoritative sites (.edu, .gov, niche authorities) boosted citation odds significantly. This suggests that all the traditional trust signals – quality backlinks, author expertise, site reputation – remain crucial or are even amplified. If the AI is essentially “choosing teammates” to help answer a question, it will choose sources it deems reliable. So SEO strategy should double-down on building authority: publish expert content, get quoted or linked by trusted publications, and showcase your credentials.
- Structure and Schema Markup: The way you structure your content can directly influence whether AI models “see” and use it. AI systems (and search crawlers) love content that is easy to parse and extract. Using clear headings (H2, H3) to break down sections, bullet points, and numbered lists to highlight key points makes it more likely the AI will grab that text for an answer. Think of it this way: if the AI is scanning your article for the specific answer to a sub-question, a well-structured piece with obvious sections (like an FAQ section or clearly labeled steps) is low-hanging fruit to pull from. Additionally, adding schema markup (structured data) like FAQ schema, HowTo schema, etc., provides machine-readable cues about your content. There is evidence that FAQ and How-To schema helped AI tools identify answer-worthy content. For instance, marking up a frequently asked question on your page might make it easier for Google’s AI to recognize that your page directly answers that question and thus cite it. As a strategy, ensure your content management system takes advantage of relevant schema (FAQPage, HowTo, Article with author markup, etc.). It could be the difference between the AI paraphrasing your answer without credit vs. quoting your answer with a citation.
- Freshness Counts: Google’s AI has access to real-time information and tends to prioritize up-to-date content when relevant. One finding was that about 75% of sources cited by AI had been updated in the last 6 months. Freshness is seen as a proxy for relevance and accuracy in fast-changing topics. For SEO, this means you can’t just publish and forget – a regular cadence of updating your content (adding new stats, current examples, 2025 updates, etc.) can signal to the AI that your page is current and worth including. This doesn’t mean old evergreen content is useless; it means consider adding a paragraph or two of updates or using a “last reviewed on” date if possible. A practical tip is to audit and refresh your high-value content at least quarterly. Not only could this help with AI citations, but human users also prefer up-to-date info, which indirectly might lead to better engagement signals.
- The “Unique Insight” Advantage: AI models often generate generic text from widely available info. So when they look for sources to cite, providing unique value or data makes your content stand out. If every site has the same generic advice, the AI might just synthesize it and not bother citing anyone. But if you have something distinctive – e.g., original research, case studies, expert quotes, proprietary data, or a novel take – the AI is more likely to quote or reference you directly (because it can’t get that info elsewhere easily). One analysis noted that “generic advice gets rewritten; unique insights get cited.”. For example, a blog post that includes an original survey result (“Based on our survey of 1,000 customers, we found X…”) or a unique infographic/chart was often directly quoted by AI answers. So, as an SEO tactic, invest in creating content that has something new to say – this could be your own small research, personal stories, or community-sourced insights. Not only does this help with AI citations, but it also differentiates you to human readers.
- Focus on Topics (Clusters) Rather than Individual Pages: AI Mode’s fan-out and reasoning means it might draw from multiple pages of yours (and others) to compose an answer. It’s looking at the “custom corpus” of relevant content. This underscores the importance of having a well-organized cluster of content around your niche. For example, if you run a cooking blog and want to be the go-to source for bread baking questions, it helps to have a cluster of pages: a sourdough starter guide, a yeast troubleshooting FAQ, a recipe for basic bread, etc., all interlinked. This breadth signals to Google’s AI that you have deep knowledge in this area. It might pull a tip from one page of yours and a definition from another. From an SEO perspective, ensure internal linking is strong and your site has comprehensive coverage of the topics you want to be authoritative on. The AI might effectively treat your site as one resource (one large knowledge base) rather than evaluating just one page in isolation as before.
- Personalization and SEO: Since AI Mode can personalize results, traditional “rankings” become fluid. It’s possible that for User A, your site is cited as a source, but for User B (different profile), it’s not – even with the same query. Google’s use of user embeddings (profiles) means we may need to consider how our content resonates with different audience segments. Practically, this could mean if you serve different demographics, having content (or angles) that appeal to each can help you be included more often. For instance, a finance site might have one article on “investing in your 20s” and another “investing in your 50s” – the AI might cite one or the other depending on the user’s age it infers. It’s a bit speculative, but worth considering segment-specific content if relevant to your business.
In summary, classic SEO best practices are still very much in play – quality content, authoritative backlinks, clean site architecture, etc., haven’t lost importance. What’s changed is how Google evaluates what is “the best answer.” It’s not just about the single page with the best optimization; it’s about the collection of evidence your content provides to the AI. SEO in the AI era is about being the best supporting resource for the AI’s answers. As Mike King (iPullRank) noted, visibility is now a vector – it’s multidimensional and probabilistic. So, focus on overall topical authority, structure, and originality to increase the probability that your content gets woven into the AI’s responses.
Impact on Content Formats (Blog, Video, Interactive Content)
Google’s AI Mode being multimodal means it can tap into various content formats, and Google itself is nudging creators to produce a mix of text, video, images, and more. Let’s break down how different content formats fare:
- Blog/Article Content: Written content remains fundamental, as it’s the easiest for AI to parse for direct answers. Well-written articles, guides, and blog posts will continue to be a primary source of information for AI Mode. However, the way those articles are used might shift. Instead of someone reading your 2,000-word blog post, the AI might extract the two sentences that answer a specific question from it. This means each section or paragraph of your article should be crafted as if it might stand alone. Ensure clarity and completeness in each thought. Also, consider adding concise summaries or key takeaway boxes in your posts – these are likely targets for AI summarization. Long-form content that is thorough (think 1,800+ words covering subtopics) tends to do well in being cited, because the AI finds a lot of relevant material in one place. So, comprehensive blog posts (as long as they remain well-structured and not rambling) can be very effective.
- Video Content: YouTube and video content can be surfaced by AI Mode thanks to transcription and understanding of video context. For example, if someone asks a “how to” question, AI Mode might actually pull insights from a popular YouTube tutorial on the subject (Google owns YouTube, so this integration is likely strong). We might see the AI answer include a key point from a video, or even suggest: “Here’s a quick tip from [Person]’s YouTube video on this topic.” To leverage this, content creators should consider providing transcripts or detailed descriptions of their videos, which improve the AI’s ability to know what’s in them. Also, ensure your video titles and descriptions are clear and keyword-rich for the topic. If you’re a small business, creating short explainer videos or demos could increase your chance to be referenced in answers for relevant queries (and if the user is interested, they might click through to watch it). Google’s encouragement of varied formats means having both an article and a video on a topic might give you double the exposure: the text could be cited and the video could be suggested or even embedded.
- Images and Visuals: AI Mode can show images as part of answers when appropriate. Google has been developing AI that can create custom data visualizations on the fly, and they’ve mentioned bringing custom data visualization to the SERP based on your data. That suggests if your site provides a useful chart or infographic (or underlying data), the AI might generate a similar visual to present to the user. It’s possible that the AI will credit the source of the data or image. For instance, if you publish a compelling infographic about social media usage, the AI might display it or recreate it and cite your brand. Content like original charts, graphs, or illustrations could thus become traffic drivers indirectly (users see your chart via AI and associate the info with your brand). Make sure any visuals you create are high-quality and have proper metadata (alt text, captions) describing what they show, so AI understands them. Also, including your logo or brand name on images (tastefully) can ensure that even if the image is shown outside your site, viewers know the source. A practical tip: incorporate key data points in a visual format in your content; AIs often quote data, and if accompanied by a chart, that’s even better.
- Interactive Content and Tools: AI Mode’s advent means some traditionally website-based interactive experiences might be answered directly. For example, instead of going to a mortgage calculator on your site, a user could ask the AI “What would my mortgage payment be on a $300k loan at 4% for 30 years?” and the AI will calculate it and give the answer, possibly citing a source or calculator. If you provide calculators, quizzes, or other tools, think about how to remain relevant. One approach is to offer unique interactive experiences that AI can’t easily replicate with a quick answer. Alternatively, ensure the AI knows about your tool – if it’s the best of its kind, the AI might direct users to it (e.g., “Use this tool on ExampleSite to get a detailed calculation”). Also, consider integrating with Google’s ecosystem if possible (for instance, through Google’s programmable search or datasets). On the positive side, if AI Mode includes “agents” that perform tasks, partnering with Google’s systems could funnel transactions to you. For example, if you’re a booking platform and Google’s AI agent can book through your API, you still get the business, even if the user never saw your site’s front page. This is more for bigger partners currently, but it’s where things are headed.
- “Non-Commodity” Content and Short Lifespan: One concern raised in the SEO community is that “non-commodity” content might not have a long lifespan in AI Mode. Commodity content is generic info anyone can provide (like “how to boil an egg”). Non-commodity content is unique – say, your personal experience story or a proprietary study. While unique content is great for citations, ironically once it’s digested by the AI, it might reduce the need for the user to read the full piece. Google is effectively remixing content on the fly (and they’ve even hinted at potentially using tools like Veo or Imagen in the future to generate new visuals or formats from your content). This suggests that any content format that can be easily transformed or summarized by AI will be – meaning users might not consume it from the source. It puts pressure on content creators to continually innovate and produce fresh, unique pieces to stay ahead. If you publish one great infographic, the AI might show it and then everyone’s seen it – what next? The shelf-life of content might shorten unless it’s continuously updated or expanded.
In effect, the best strategy is to diversify your content formats. A mix of in-depth articles, engaging videos, clear infographics, and handy tools will cast a wide net. Google’s AI Mode can pull from any of these, so the more formats you have covering a topic, the more “entry points” for the AI to include your brand. Also, different users prefer different media – some will still scroll down and watch the video even if the AI gave a text summary, etc. By providing multi-format content, you cater to those who choose to click through.
Lastly, note that Google Search Console will likely start showing data for AI Mode impressions and clicks (combined across formats). Keep an eye on that to see which content formats on your site are getting visibility via AI. For example, if you see your videos popping up as traffic sources or your images in Google’s stats, that’s a clue those formats are resonating.
Impact on Engagement & Brand Discovery
AI Mode changes how people discover brands and engage with content, in large part because the AI intermediary can both help and hinder visibility. Here’s what to consider regarding audience engagement and brand discovery:
- Brand Mentions as the New Click: In the past, a user might discover your brand by clicking your site from search results and browsing around. Now, a user could hear about your brand from Google’s AI answer without ever clicking immediately. For example, an AI response might say, “Several fitness experts like TrainerJohn from FitLife.com recommend alternating cardio and strength training.” That user just learned of “FitLife.com” and a trainer’s name through the AI’s citation. This kind of implicit brand endorsement can be powerful. It’s almost like word-of-mouth via AI. Users may not click right then, but the next time they see your brand (or even as they continue the conversation, they might ask, “Who is TrainerJohn?”), you have a recognition advantage. As Ahrefs’ large study showed, “brand web mentions” have the strongest correlation with being included in AI Overviews. In fact, they found branded mentions on the web correlated far more with AI visibility than traditional SEO metrics like backlinks did. The top three factors correlated with appearing in AI results were all related to brand presence: how often your brand is mentioned on the web, in anchor text, and how many people search for your brand. This means building your brand’s footprint (PR, social buzz, being referenced in articles, etc.) is directly tied to discovery in AI Mode. If your brand is relatively unknown, the AI might lean toward citing more established names in your niche that it “trusts” users will recognize or that its algorithms deem authoritative.
- Trust and Engagement Without Clicks: User engagement with your brand can start right on the SERP now. Imagine a user asks the AI a question, and your site is cited multiple times in the AI’s response. That repetition can instill trust – like “this brand keeps coming up as a source, they must know their stuff.” So by the time the user does click (maybe on a more specific follow-up query), they are already somewhat warmed up to your brand. Alternatively, even if they don’t click in that session, they might recall your brand name later when they have a related need (“I remember FitLife.com was mentioned a lot for workout advice, let me go there directly”). This is a new kind of engagement funnel: impression -> mental recall -> later direct visit, rather than just impression -> immediate click.
- Deeper Engagement on Click: When users do click through from an AI result, they often have a more specific intent (as discussed under traffic quality). Businesses should be prepared to capture that engagement immediately. If someone comes from an AI answer looking for details, make sure the page they land on delivers depth (since the basics were already covered by the AI). These visitors might scroll more and read longer, because they came for the nitty-gritty. Ensure your content anticipates that. For example, if the AI summarized “5 tips to save on taxes” from your site, and the user clicks your site, they likely want more examples or a step-by-step guide. If you only had those 5 tips and nothing more, they might bounce. Consider adding layers of detail: a concise summary (for AI and quick readers) and expandable sections or downloadable resources for those who want to go deeper. This can improve on-site engagement metrics and conversions once a user is on your site.
- New Forms of Interaction – Agents and Conversations: With AI Mode’s upcoming agentic features, user engagement might sometimes skip visiting your site altogether, yet still result in a conversion or lead for you. For example, if you run a local service business (say a spa or a restaurant), a user could interact with Google’s AI to find and book an appointment, and Google’s agent might book it through your scheduling system. The user may only see a confirmation, having never visited your homepage or booking page manually. From the user’s perspective, they engaged with Google, but in reality they engaged with your service via an API. Businesses need to be aware of this shift: ensure your business information, inventory, or booking capabilities are integrated with Google’s platforms (Google Business Profile, Reserve with Google, etc.). That way, when AI agents look to fulfill a request, your business can be an option. Failing to integrate could mean you’re invisible to these AI-driven transactions, and someone else gets the booking.
- Loss of Certain Engagement Opportunities: On the flip side, since AI provides answers immediately, users might not engage in some of the ways they used to. For instance, they might not scroll through forums or comments (the AI might have already compiled the wisdom from a long forum thread into a neat answer). If your content strategy relied on, say, users reading a blog then signing up for a newsletter via a sidebar form, realize that in AI Mode they might never see that call-to-action. The AI doesn’t (currently) tell the user, “hey subscribe to that site’s newsletter.” So we might need to find new ways to prompt engagement. One idea is to incorporate calls-to-action within the content that’s likely to get cited. For example, a line like “(You can download our free checklist for more details)” might or might not be included in what the AI shows. Likely it won’t include an overt CTA. However, if a user clicks through for more info, having a strong, immediate CTA on your page becomes crucial because you might only get one pageview from them. Optimize landing pages (the pages people land on from AI citations) to capture interest quickly – with clear offers, email signups, or whatever next step you want, since they might not browse around as much.
- Social Proof & Community: With less direct traffic, you might see lower comments on blogs or fewer forum interactions on your own site because people got their answers from AI. To keep a sense of community and engagement, you may need to foster it off-site or in other ways (like engaging on social media where people discuss the information). Alternatively, incorporate interactive elements on your site that AI can’t replicate, such as community Q&A sections or live expert chat. If the AI gives the quick answer, maybe users will come to your site for the discussion or personal connection. Emphasize what’s beyond the answer – for example, a support community, user stories, or an interactive tool that the AI can’t fully provide.
- Brand Differentiation: In a world where AI summarizes everything, brands risk becoming faceless sources unless you actively differentiate. Your brand’s voice, story, and unique perspective need to be clear in your content. While AI might strip away some of that in the immediate answer, if a user is intrigued enough to explore more, having a memorable brand identity will stick. Moreover, if many brands publish similar info, the AI might gravitate to the one with the strongest brand signals (as noted with web mentions and search volume correlation). This implies a cycle where the rich get richer: known brands get cited more, which makes them more known. A small business should invest in brand marketing (PR, social presence, maybe even traditional media) so that its name carries weight. This isn’t the old-school SEO advice, but in the AI era, the algorithms are looking at overall brand presence as a trust factor. The Ahrefs study noted brands that earned the most web mentions got up to 10× more AI mentions than the next tier. So, engaging in your industry (guest posting, being on podcasts, sponsoring webinars, etc.) to boost your brand mentions can indirectly boost your AI visibility.
In essence, brand discovery is becoming more indirect – via mentions and citations – and engagement may not always happen through the traditional website journey. Business owners should adapt by treating the AI as a new “audience” that needs to know about their brand (through factual mentions, schema, etc.), and by optimizing the limited touchpoints where a user does interact with you directly (be it a single page visit or a seamless transaction via Google). Focus on brand-building and trust, because AI will pass those signals on to users.
Impact on Lead Generation Funnels
Lead generation – guiding prospects from awareness to interest to conversion – is fundamentally affected by AI Mode because the top-of-funnel and even mid-funnel stages can happen without the user on your site. Here’s what changes and how to adapt:
- Shortened Funnels: With AI delivering immediate answers, users might bypass the early informational touchpoints that businesses traditionally used for lead generation. For example, in a classic funnel, a user searches a broad question (“What is CRM and why do I need it?”), reads your blog post, becomes interested in your CRM product, then later perhaps signs up for a newsletter or free trial. In AI Mode, that user might get the general answer from Google’s AI – possibly even with a generic list of top CRM tools – and only engage with a product site when they are ready for a free trial. The research phase is being handled by AI in many cases. This means by the time a lead lands with you, they might be later in the funnel (which is good, they’re more qualified), but you might have lost the chance to nurture them earlier with your content offers. To adapt, align your content and offers to capture leads at the point of need. If they skip straight to comparing products, ensure you have comparison pages or decision guides that the AI might reference or that rank well if they dig deeper. Also, integrate lead magnets into pages that are likely landing points from AI queries. For instance, if your broad “What is CRM?” post won’t get the traffic, make sure your more specific “CRM implementation checklist” (something a user might seek after the initial question) is excellent and perhaps offered as a downloadable PDF on your site. The AI might not deliver the PDF, but it could bring the user to the page where you offer it.
- AI as the New Middleman: In some scenarios, Google’s AI might become an active part of your funnel. If a user expresses a desire or intent (“I need a project management tool for a 5-person team”), the AI might both recommend solutions and facilitate the next step. Google could show an AI-curated list of options (with summaries) rather than the user reading 5 different product pages. If you’re in such a space, providing structured data about your product (features, pricing tiers, etc.) is critical so Google’s AI has accurate info. We’ve also seen Google integrating things like “chat with the site” or “check availability” in some contexts – AI Mode might let users ask follow-ups specifically about your product or service via the AI. For example, after an AI mentions your SaaS as an option, the user could type, “Ask [Your Company] if they integrate with Shopify,” and the AI might retrieve that from your FAQ or even prompt an AI chatbot on your site if available. To capture leads, ensure that wherever the AI might direct them next, you have a clear call-to-action. If AI provides a comparative answer and then suggests “You can learn more on their official site,” your site’s landing page should immediately offer a free demo or trial sign-up since the user is likely evaluating options at that stage.
- Conversion Actions Within AI Mode: As previously noted, Google is exploring letting users complete actions via AI (transactions, bookings, sign-ups). In terms of lead gen, this could mean a user might join a webinar or subscribe to a newsletter through prompts without visiting your site directly (for example, the AI could say “Would you like me to sign you up for a free whitepaper from CRMco?” and do it if the user agrees). While this specific scenario is speculative, the pieces (Google’s AI, Gmail integration, etc.) exist. It underscores the importance of providing easily accessible APIs or integration points for Google to interface with your systems. At the very least, keep your Google Business Profile and other Google-linked assets up to date, as some lead actions (like appointment bookings or requests for quotes) can already happen through Google’s interface.
- Measurement and Attribution Challenges: Lead tracking is going to get trickier. If a user learned about you via an AI answer on Monday, then on Friday directly typed your website and converted, traditional analytics may mark that as “direct traffic” or organic, but you wouldn’t realize the AI citation played a role. We may need new attribution models that account for AI touchpoints. Google adding AI Mode data to Search Console is a start. For now, a practical approach is to monitor overall brand search volume and direct traffic – increases there might indicate that the AI is boosting your brand awareness upstream. You can also experiment with unique promo codes or URLs mentioned in content; though AI might not repeat those verbatim, you could attempt to see if an AI summary sometimes includes, say, your product name + model or some clue that drives people to search that. This is an emerging area, so be prepared for a bit of darkness in funnel analytics – you might not fully see how a lead found you. Focus on making your brand and value proposition clear in any context so that whenever a user decides to seek you out, they know what to do.
- Top-of-Funnel Content Still Matters (But in a Different Way): You might be wondering, if AI is answering basic questions, should I still create informational, top-of-funnel content? The answer is yes, but with a twist. You still need that content for the AI to draw from (and for the segment of users who do click through). But you might adjust your approach: more collaboration, less gating at the top. For instance, instead of expecting a beginner’s guide to directly capture a lead via a form, use it to get cited and build trust, and have more in-depth follow-ups ready. Also, you might optimize some of those pieces to appeal to the AI’s “liking.” For example, a broad explainer might intentionally have a paragraph that succinctly defines the concept (for the AI to grab), followed by your brand’s take or a case study (which might not be in the AI answer but can hook a human reader). This way, the AI uses your factual info, and if a user clicks, they get into the narrative that leads to your solution.
- Lead Magnet Placement: Traditionally, many sites offer a lead magnet (ebook, checklist, trial) after warming up the user with content. In AI Mode, the “warming up” might have happened off-site via the AI. When the user arrives at your site, they might be ready for the offer sooner. Don’t hesitate to present a relevant offer quickly on pages that AI traffic commonly lands on. Use tools to see which queries or pages are getting AI references (when available) and tailor those pages to convert. For example, if your page on “SEO checklist 2025” is frequently cited, make sure that page invites the visitor to download a fuller checklist PDF or sign up for an SEO webinar – something that captures the lead right away. Users coming from an AI citation may not browse around, so give them the next step upfront.
In summary, the lead generation funnel is compressing. Awareness is often happening via AI mention, consideration might happen partially through AI comparisons or fewer website visits, and conversion might be more directly pursued by the user once they engage. Business owners should streamline their funnels accordingly: remove unnecessary hurdles, ensure your key value propositions and offers are immediately visible, and consider the AI as a new top-of-funnel channel. The classic marketing advice of being where your customers are now extends to being where the AI is – meaning ensure the AI has your information to hand off to customers.
Next, let’s consolidate some actionable strategies given all these changes.
Strategies for Content Creators & Small Businesses to Adapt
Adapting to Google’s AI Mode requires both technical optimizations and strategic shifts in how you approach content and marketing. Here are clear, actionable strategies to remain discoverable and valuable:
Optimize for AI Visibility (AI-SEO Tactics)
- Aim to Be the Cited Source: Structure your content to directly answer common questions in your niche. Use an FAQ style or dedicate a paragraph to likely questions (with clear headings). This increases the chance the AI pulls your text as a quote. For example, start a section with “Q: What is X?” and follow with a concise answer. Many publishers find their FAQ pages are getting cited by AI summaries. This also means using schema (FAQPage, etc.) to flag those Q&As to Google.
- Deep, Comprehensive Content: As noted, content that covers a topic in-depth (roughly 1,800+ words, covering subtopics thoroughly) was more likely to be cited by AI. Don’t shy away from long-form content as long as it remains useful. Provide a rich resource that an AI (and a user) could consider one-stop for that subject. Consider adding a table of contents at the top for usability (the AI might even use the anchor links internally).
- Bolster E-E-A-T: Make your expertise visible. Include author bios with credentials on your articles (e.g., “Jane Doe, 10-year Certified Nutritionist”). If you have experts, have them write or at least review content (and mention that). Cite credible sources in your content as well – being well-referenced yourself can signal that your content is research-backed. Also, get mentions or links from authority sites (industry associations, news, .edu sites). This isn’t new SEO advice, but it’s increasingly important because the AI looks for trust signals. If you’re a local business, encourage reviews and mentions in local press or community sites (those count as web mentions/authority in your sphere).
- Keep Content Fresh: Create an editorial calendar to update key pages. Even small updates (new statistics, a 2025 note, a recent example) can reset the freshness clock. When updating, you can mention “Updated on [Date]” on the page – the AI might pick up on that recency. Also, tackle trending questions in your industry with blog posts; being among the first to answer a new question can get you cited before others catch up.
- Use Clear Structure & Formatting: As a rule, make your content skimmable. Use descriptive headings (H2, H3) that include the question or the main point of the section. Utilize bullet points or numbered steps for procedures or lists – AI answers often like to output as lists and may use your formatted list directly. For example, “5 Steps to Do X” with steps 1-5 laid out clearly. Ensure images have alt text that describes them (in case AI reads that to understand the image) and captions if needed.
- Leverage Schema Markup: Implement relevant schema for your content type:
- FAQ Schema: For Q&A content.
- HowTo Schema: For step-by-step guides.
- Article Schema with Author: to highlight author credentials.
- Product and Review Schema: if you have products, so AI can pick up specs or ratings.
- FAQ Schema: For Q&A content.
- Proper schema helps Google understand the context and might be used in AI reasoning. It’s like speaking the AI’s language about your content’s purpose.
- Monitor AI Citations: Currently, tracking when and where your site is cited by AI is tricky. But you can gather some insight by looking at Search Console (once AI Mode data is included) or using third-party tools that monitor AI results. If you find that certain pages get cited, analyze why (do they have certain structures or info?). Conversely, if important content never gets cited, see if you’re lacking something (maybe the answer isn’t clear or someone else’s content is preferred). This will help refine your approach. Some SEOs suggest using tools or prompt engineering to simulate what questions your content could answer – essentially predict the “query fan-out” and ensure you cover those angles in your content.
Adapt Content Strategy and Planning
- Map Out User Questions and Journey: Put yourself in your audience’s shoes and list the questions they have at each stage of their journey. Ensure you have content that addresses all those questions. Remember, if you don’t have it, the AI will find it elsewhere. For each broad topic, brainstorm the likely follow-up questions (the AI certainly is doing this via fan-out). Use tools or even Google’s “People also ask” and forums to find these. Then either create new content or incorporate answers into existing content. This holistic coverage makes you more likely to be referenced multiple times in a conversation.
- Invest in Unique Research or Data: As mentioned, bring something new to the table. Conduct a small survey in your customer base, compile industry stats into a unique index, or analyze your own data and publish findings. Even a blog post like “We analyzed 1,000 cases and here’s what we found…” can set you apart. AI loves to cite specific data points (since they add credibility to its answer). If you’re the source of “37% of consumers prefer X,” and that’s relevant, you’ll likely get cited. This not only feeds the AI, but such content often earns backlinks from others as well, strengthening your authority.
- Create Multi-Format Content Hubs: Don’t rely on one format. For your key topics, create a content hub that includes a pillar article, infographics, a video, maybe a podcast episode transcript, etc. Interlink them. This way, whether the user (or AI) prefers text, visual, or audio, you have something to offer. Google’s AI might show a mix (text answer with a suggested video). If all the content in that answer is essentially yours (text from your article, and your YouTube video suggested), you’ve dominated that result. It’s about being everywhere the AI might look for answers.
- Speed and UX Still Matter: If a user clicks through to your site from AI Mode, you’ve piqued their interest – don’t squander it with a slow or cluttered site. Make sure your page loads fast (Core Web Vitals are still in play) and is mobile-friendly, as many users might be on mobile when using conversational search. Also, consider that if the AI result satisfied a lot of the curiosity, the user might have a specific goal for clicking – make it easy to find or do that on your page. For example, if they clicked because they want an example or case study, maybe have a highlighted case study section instead of burying it. A good user experience increases the chances they’ll stay and perhaps convert.
- Engage Users Beyond Google: To mitigate dependency on search, strengthen other channels of engagement. For instance:
- Email Newsletters: If users do come to your site, encourage them to subscribe so you can reach them directly with content (bypassing Google next time).
- Community Building: Whether it’s a Facebook group, Discord, Slack community, or forums, give your audience a place to ask questions and discuss. It might sound counterintuitive in an AI era, but humans still seek community. If some of that shift away from search happens, you want to catch those who prefer asking peers or experts in a community.
- Social Media and Content Repurposing: Share snippets of your content (the unique insights, tips, etc.) on LinkedIn, Twitter, etc., to build your brand presence (those mentions out in the wild web also boost the chance AI sees your brand). Being active on Q&A platforms (like Quora or Reddit, where appropriate) can also help – sometimes AI even trained on those types of content. Plus, the more people talk about your brand online, the more it feeds the signals the AI uses.
- Email Newsletters: If users do come to your site, encourage them to subscribe so you can reach them directly with content (bypassing Google next time).
- Align with Google’s Tools: Pay attention to Google’s own features for businesses. For example, if you’re e-commerce, ensure your products are in Google Merchant Center so that if AI Mode shows shopping info or does a price analysis, your products are included. For local businesses, use Google Business Profile fully – update Q&As there, because AI might pull from that in local context. Essentially, keep your “official” data in Google’s ecosystem accurate (feeds, listings, schemas) so the AI has the best info to work with.
- Be Prepared for Change: The AI search landscape is evolving rapidly. Google is experimenting and may adjust how AI Mode works (which queries invoke it, how it presents sources, etc.). Stay informed via reliable SEO news sources (like Search Engine Land, Search Engine Roundtable, etc. – two of the sources of info for this report). Google may also release guidelines specifically for AI visibility. Adaptability is key: what works to get cited today might shift if Google tweaks the algorithm or users change their behavior. For instance, if you notice users start phrasing queries differently with AI (“longer, more conversational queries”), consider incorporating those natural language phrases in your content (in a Q&A format, for example). One observation is that queries are indeed getting longer and more conversational with AI – e.g., instead of “best shoes basketball”, users ask “What are the best black or gray basketball shoes under $60 for a 40-year-old with bad knees?”. That’s the kind of verbose query AI invites. You might not optimize for that exact query, but be aware that content needs to cover very specific combinations of requirements to satisfy such detailed questions.
To synthesize these strategies, here’s a quick-reference list of critical takeaways and tips:
New Search Behaviors (AI Mode) – What to Know & Do:
- Users ask more detailed, conversational questions (often multi-part).
→ Ensure your content addresses specific scenarios and sub-questions. Consider adding Q&A sections. - Fewer users click results for simple queries (the AI gave them the answer).
→ Track which queries lose traffic. Provide value beyond the basic answer (tools, deeper insights) to entice clicks. - Users trust AI’s cited sources similarly to how they’d trust top search results.
→ Being cited is the new “ranking high.” Focus on content quality to earn those citations. - Some searches become interactive tasks (booking, buying via AI).
→ Integrate your business with Google’s services (Google Reserve, etc.) so AI can transact with you. - Search is more personalized per user; results can vary widely.
→ Diversify content to cater to different personas. Build brand loyalty so users specifically seek you out.
SEO Adaptation Tactics for AI Mode (AI-SEO):
- Content Depth & Quality: Publish comprehensive, well-researched content (aim for covering subtopics; ~1800+ words often cited).
- E-E-A-T Signals: Highlight expert authors and accurate info. Earn authoritative backlinks and mentions.
- Clear Structure: Use headings, lists, and schema (FAQ, HowTo) to make content AI-friendly.
- Freshness: Update content regularly; AI favors recent info (majority of AI-cited pages updated <6 months).
- Unique Insights: Provide original data or perspectives; AI will quote unique stats or examples.
- Internal Linking: Link related content on your site to reinforce topic clusters (AI might traverse your content network).
- Monitor & Iterate: Watch for AI Mode in Search Console data. Adjust content that isn’t getting visibility (maybe it needs more clarity or substance).
Content Planning Recommendations:
- Multi-Format Content: Create articles, videos, infographics on key topics – serve both the AI’s needs and user preferences.
- User Journey Mapping: Identify questions at each stage (awareness to decision) and ensure content exists for each.
- Lead Capture Optimization: Make every page that users land on from AI have a clear next step (CTA, signup, offer) since you may get only that one chance.
- Brand Building: Spend effort on PR, guest posting, social media to increase web mentions of your brand (strong correlation with AI visibility).
- Community & Loyalty: Build direct channels (email, communities) to engage users so you’re not solely reliant on Google’s AI to reach them.
- Technical Prep: Implement structured data, ensure mobile speed, and integrate with Google’s business features (so AI has the best access to your content and services).
By following these strategies, content creators and small businesses can better align with the new AI-driven search landscape. Rather than fearing the changes, savvy businesses will use them as an opportunity – for instance, becoming the go-to authority that Google’s AI relies on, or leveraging improved targeting of serious buyers who click through. The key is to stay informed, remain flexible, and keep the focus on delivering real value to users (human and AI alike). After all, Google’s goal (AI or not) is to serve users the best information and solutions – if you position yourself as the provider of those, you stand to gain even in this new environment.
Google’s AI Mode vs. Bing Copilot vs. Perplexity: A Brief Comparison
Google isn’t the only player incorporating AI into search. Competitors like Microsoft’s Bing (with its AI “Copilot” chat) and independent AI search tools like Perplexity.ai have also been offering AI-assisted search experiences. Here’s how Google’s AI Mode stacks up and what that means for content creators:
- Bing AI (Bing Chat/Copilot): Bing integrated OpenAI’s GPT-4 model into its search in early 2023, providing a chat sidebar that could answer queries with cited sources. In many ways, Bing’s AI chat is similar to Google’s AI Overviews/Mode: you ask a question, it gives an answer with footnoted links. Bing’s AI can also handle follow-up questions and even generate images on demand (via DALL-E integration). However, Bing’s approach to personalization is less extensive than Google’s – Bing might use your Microsoft account data in a limited way, but it’s not (currently) pulling from your emails or deeply integrating with personal calendars like Google plans to. Bing does, on the other hand, have the advantage of being more publicly accessible earlier; a lot of users and thus businesses have some experience with how it cites content. If you optimized for featured snippets in the past, Bing’s AI likely has cited you if you were a top result for a question. Strategies to appear in Bing’s AI answers are largely the same: good content, SEO best practices. One thing to note: Bing’s user base is smaller than Google’s, but if Google’s AI mode reduces some traffic, Bing might become relatively more attractive as an SEO traffic source. So don’t ignore optimizing for Bing (which often just means the same good content practices). Bing’s “Copilot” name also extends to Windows and Office integration – meaning content might be surfaced in contexts beyond the browser (like answering questions inside Word, etc.). Ensure your content can be easily found and read by Bing’s crawler as well (submit your site to Bing Webmaster Tools).
- Perplexity.ai and Other AI Search Tools: Perplexity is an AI search engine that provides direct answers with citations, somewhat like a mini Google+ChatGPT combined. It often pulls from a curated set of high-authority sites (including Wikipedia, major news sites, etc.) to answer questions. Perplexity has a growing user base of those who like quick answers with sources. For content creators, being cited in Perplexity means similar tactics: have authoritative content that directly answers questions. It might weigh things a bit differently (perhaps more weight on well-known sources). While you can’t optimize for every single AI search startup (there’s also YouChat, NeevaAI – though Neeva shut down consumer search – and others), the general rule is the more authoritative and well-cited your content is on the open web, the more likely these models will use it. Also, these tools often use Wikipedia and a knowledge graph heavily – which means it’s worthwhile to have your brand or key topics well-represented in Wikipedia or other knowledge bases (Wikidata, etc.) if possible. For example, if you have a notable business, ensuring it has a Wikipedia page (adhering to their notability rules) can help AI tools recognize and possibly favor information related to your brand.
- Google AI Mode’s Unique Edge: The biggest difference is Google’s AI Mode ties into Google’s vast ecosystem (Search, Maps, Shopping, etc.) and personal data (with permission). Neither Bing nor Perplexity has the same breadth of real-time data integration. Google can pull in live info (stock prices, local store inventory, etc.) directly. It also has the Knowledge Graph and years of search intent understanding. So Google’s answers might be more context-rich, and for businesses, Google’s AI Mode might favor content that is integrated with those services. For example, if someone asks a shopping question, Google AI can not only cite reviews (content sites) but also list products (with links to Google Shopping listings). Bing can show shopping results via its partnerships, but Google’s is more native. Perplexity doesn’t do commerce integration at all, it just gives info. So for a business, Google’s AI could be both information provider and marketplace – citing a blog and then suggesting “buy this product here” with a link. It’s crucial to have presence in both content form and product schema/feeds for Google.
- Citation Patterns: Bing’s AI and Google’s AI might cite somewhat different sets of sites at times. Some SEO studies suggest Bing’s AI was more likely to cite forums or more conversational sources earlier on, whereas Google’s tends toward more official sites or structured info sources. Perplexity often cites community Q&A (StackExchange, Reddit excerpts) because it tries to find direct answers. What this means: a diversified content strategy (including participating in Q&A forums, and having content on your own site) can cover all bases. If a question is often answered on a forum and you have an expert answer there, Perplexity might pick it up. Meanwhile, Google might cite your polished blog answer.
- Adoption and User Base: As of 2025, Google Search is still the behemoth. AI Mode being available to all US users means a massive potential reach. Bing’s share has grown slightly with their AI feature, but it’s still much smaller. Perplexity and others are niche players. So, prioritize Google’s AI Mode in your strategy, but where feasible, test how your content appears on Bing’s AI or Perplexity. For instance, search your question on Perplexity – see if you show up. It can be insightful; if not, who is showing up? Perhaps you can aim to create content similar to what they cite (if it’s high quality).
In summary, Google’s AI Mode is the most integrated and potentially disruptive due to Google’s reach and data. Bing’s AI is similar in concept and you should follow best practices to capture that traffic too. Perplexity and others reinforce the same lesson: high-quality, trusted content wins across these AI platforms. If you’ve adapted well for Google’s AI, you’ve likely covered Bing and others as well. However, keep an eye on Bing’s developments – Microsoft is aggressively improving its AI integration (e.g., the Windows Copilot can draw info from the web via Bing). It might send you traffic in ways we haven’t seen before (like someone using Windows Copilot to ask a question that leads them to your site). Being early to understand these alternative channels could give a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Google’s experimental AI Mode is a game-changer for search, bringing both challenges and opportunities for content creators and small business owners. By understanding how it works – from Gemini’s reasoning to query fan-out – and anticipating its effects on traffic, SEO, content formats, engagement, and lead gen, you can adjust your strategy to thrive in this new landscape. The overarching theme is quality and relevance: if you produce genuinely helpful, authoritative, and easy-to-consume content in various formats, and you align with what users (and AI) are looking for, your content can continue to attract and engage your target audience. The methods may change (fewer clicks, more citations, quicker conversions), but the goal remains the same: provide value and be visible where your customers are seeking answers. Embrace the change by becoming a trusted source that AI assistants rely on – in doing so, you ensure that when the human behind the query is ready to engage or buy, your brand is top of mind and easy to reach.
Methodology
This report incorporated insights from SEO experts and studies, including Mike King’s deep dive on AI Mode, data on AI citations from Search Engine Land’s analysis, Ahrefs’ brand visibility study, and updates on Google’s AI search rollout and Search Console reporting, among others. These sources and their key findings are cited throughout the text for reference.
Resources
- Google Blog (2025). Expanding AI Overviews and Introducing AI Mode. Retrieved from https://blog.google/products/search/ai-mode-search/
- The Verge (2025). Google Launches AI Mode to Everyone in the US. Retrieved from https://www.theverge.com/google-io/670439/google-ai-mode-search-io-2025
- iPullRank (2025). How AI Mode Works and How SEO Can Prepare for the Future of Search. Retrieved from https://ipullrank.com/how-ai-mode-works
- SEOteric Digital Marketing (2025). How to Get Cited by AI in SEO: Insights from 8000 AI Citations. Retrieved from https://www.seoteric.com/how-to-get-cited-by-ai-in-seo-insights-from-8000-ai-citations/
- Ahrefs (2025). An Analysis of AI Overview Brand Visibility Factors (75K Brands Studied). Retrieved from https://ahrefs.com/blog/ai-overview-brand-correlation/
- Search Engine Roundtable (2025). Google Confirms AI Mode Reporting Coming To Search Console. Retrieved from https://www.seroundtable.com/google-ai-mode-reporting-search-console-39468.html
- LinkedIn (2025). How to Get Your Content Cited by AI: 5 Key Takeaways. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/posts/okey-a-4b9551184_how-to-get-cited-by-ai-seo-insights-from-activity-7328003203420110848-zFqv
- iPullRank (2025). Implications of AI Mode and Personal Context – 2025 Google I/O Hot Takes. Retrieved from https://ipullrank.com/ai-mode-and-personal-context-google-io

